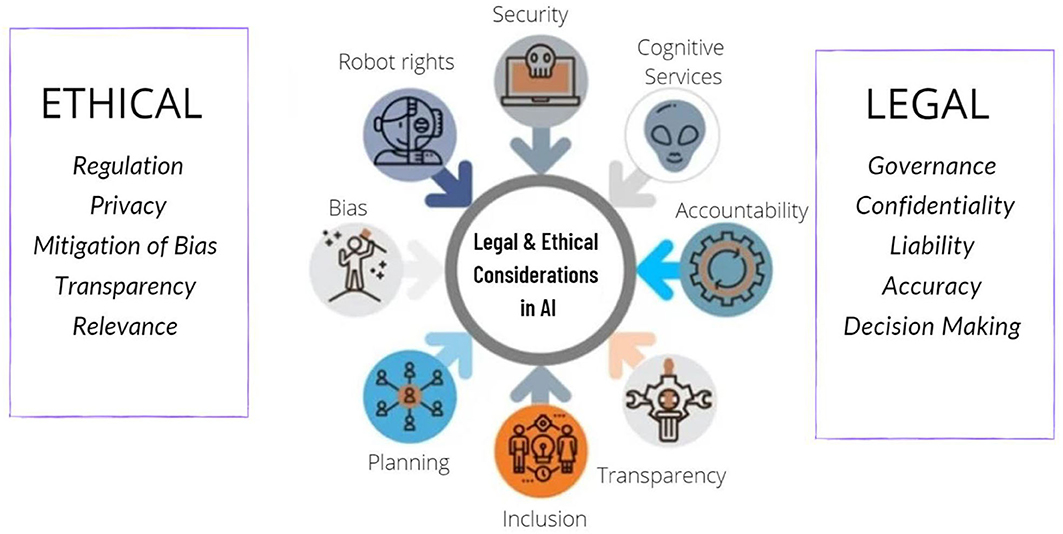
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made significant strides in health diagnostics, offering new tools for early detection, accurate diagnoses, and personalized treatment plans. The integration of AI into healthcare promises numerous benefits, such as improved diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. However, it also raises important ethical questions that need careful consideration. These concerns revolve around issues of privacy, bias, accountability, and the broader impact on the patient-provider relationship. Understanding these ethical implications is crucial for ensuring that AI technologies are implemented in a manner that respects patient rights and promotes equitable care.
Privacy and Data Security
One of the primary ethical concerns associated with AI in health diagnostics is the issue of privacy and data security. AI systems rely on vast amounts of patient data to function effectively, including sensitive information such as medical histories, genetic data, and personal identifiers. The collection, storage, and analysis of this data raise significant privacy concerns, particularly regarding how securely it is handled and who has access to it.
Ensuring that patient data is protected from unauthorized access and breaches is critical. Healthcare providers must implement robust data security measures to safeguard patient information and comply with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Additionally, transparency about how data is used and shared with AI systems is essential for maintaining patient trust. Patients should be informed about how their data will be utilized and have the opportunity to consent to or opt-out of data sharing practices.
Bias and Equity
Bias in AI algorithms is another significant ethical concern. AI systems learn from historical data, and if this data contains biases—whether related to race, gender, socioeconomic status, or other factors—the AI can perpetuate and even exacerbate these biases. For instance, if an AI diagnostic tool is trained predominantly on data from a particular demographic, it may not perform as well for other groups, leading to disparities in diagnostic accuracy and treatment recommendations.
Addressing bias in AI requires rigorous testing and validation of algorithms across diverse populations. Developers must ensure that AI systems are trained on representative datasets and regularly audited for fairness. It is also important to involve diverse teams in the development process to identify and mitigate potential biases. By prioritizing equity, the healthcare industry can work towards ensuring that AI technologies benefit all patients equally and do not reinforce existing healthcare disparities.
Accountability and Transparency
The issue of accountability is crucial when it comes to AI in health diagnostics. AI systems can sometimes make decisions or recommendations that are difficult for humans to interpret or understand. This “black box” problem, where the decision-making process of AI is opaque, can complicate efforts to hold the technology accountable for errors or adverse outcomes.
Healthcare providers and AI developers must work together to ensure that AI systems are transparent and their decision-making processes are explainable. This includes providing clear information on how AI models reach their conclusions and ensuring that healthcare professionals can interpret and contextualize AI-generated results. Moreover, establishing accountability frameworks is essential for addressing errors or issues that arise from the use of AI diagnostics. Clear guidelines and protocols should be in place to determine responsibility in cases where AI systems fail to deliver accurate diagnoses or recommendations.
Impact on the Patient-Provider Relationship
The integration of AI into health diagnostics also has implications for the patient-provider relationship. AI can enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline workflows, but it also has the potential to alter how patients interact with their healthcare providers. There is a risk that patients may become overly reliant on AI systems or feel that their concerns are overshadowed by technology.
Maintaining the human element in healthcare is crucial. AI should be viewed as a tool to support healthcare providers rather than replace them. The role of the provider in interpreting AI results, engaging with patients, and providing personalized care remains essential. Providers must ensure that they maintain open communication with patients, address their concerns, and use AI as an adjunct to their clinical expertise rather than a substitute.
Informed Consent and Autonomy
Informed consent is a fundamental principle in medical ethics, and it extends to the use of AI in health diagnostics. Patients must be fully informed about the role of AI in their diagnosis and treatment, including understanding the potential benefits, limitations, and risks associated with these technologies.
Ensuring that patients have the autonomy to make informed decisions about their care involves providing them with clear and comprehensible information about how AI is used and how it may impact their treatment. Patients should have the opportunity to ask questions and express their preferences regarding the use of AI in their diagnostics. Respecting patient autonomy and ensuring that consent is obtained transparently are essential for ethical AI implementation in healthcare.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into health diagnostics presents both opportunities and ethical challenges. While AI has the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and personalized care, it also raises important concerns regarding privacy, bias, accountability, and the patient-provider relationship. Addressing these ethical issues requires a collaborative effort from healthcare providers, AI developers, policymakers, and patients. By prioritizing transparency, equity, and patient autonomy, the healthcare industry can ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and ethically, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes and trust in the healthcare system. As AI continues to evolve, ongoing dialogue and thoughtful consideration of ethical implications will be essential for guiding its development and implementation in ways that benefit all patients and uphold the highest standards of care.