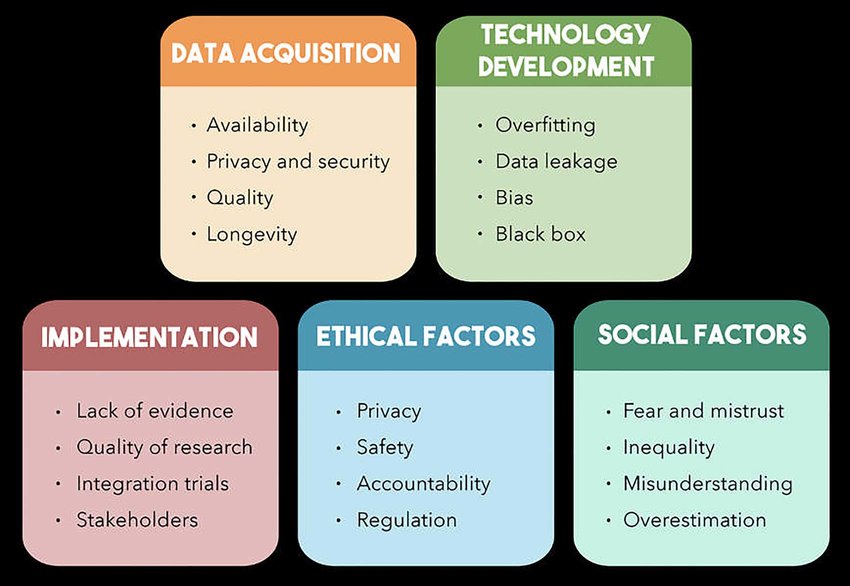
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into healthcare has revolutionized how health data is managed, analyzed, and utilized. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data and provide valuable insights has led to significant advancements in diagnostics, treatment, and patient care. However, the use of AI in healthcare also brings substantial concerns regarding data privacy. The sensitive nature of health information makes it a prime target for breaches and misuse. This article explores the drawbacks of AI in health data privacy, examining the challenges, risks, and potential solutions to safeguard patient information.
Increased Risk of Data Breaches
One of the most pressing concerns associated with AI in healthcare is the increased risk of data breaches. AI systems require access to extensive datasets, which often include sensitive personal health information. This data is stored, processed, and analyzed in various ways, increasing the number of potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
Data breaches can result in unauthorized access to patient records, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and significant harm to patients. The aggregation of data from multiple sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), wearable devices, and genetic databases, creates a comprehensive profile of individuals that, if compromised, could have far-reaching consequences. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and encryption protocols is crucial to mitigating these risks, but the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats makes this a constant challenge.
Complex Data Management and Interoperability Issues
AI systems often involve the integration of data from various sources, including hospitals, clinics, research institutions, and patient-generated data from wearable devices. Managing and integrating these diverse data sources can create significant privacy challenges. Variations in data formats, standards, and security measures among different systems can complicate efforts to ensure consistent and secure handling of health information.
Interoperability issues arise when different systems and platforms fail to communicate effectively, leading to gaps in data security and privacy. For example, data transferred between systems may be vulnerable to interception or unauthorized access if proper safeguards are not in place. Addressing these interoperability challenges requires collaboration among technology developers, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies to establish standardized protocols and ensure secure data exchange.
Potential for Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
AI algorithms are trained on historical data, which can sometimes reflect existing biases in healthcare. If the training data contains biases related to race, gender, socioeconomic status, or other factors, the AI system may perpetuate or even amplify these biases. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes, affecting certain groups of patients more adversely than others.
From a privacy perspective, biased algorithms can also exacerbate disparities in data protection. For instance, if an AI system disproportionately targets specific demographic groups for surveillance or monitoring, it may lead to privacy violations and unequal treatment. Ensuring that AI models are developed and evaluated with fairness and inclusivity in mind is essential to preventing discriminatory practices and protecting the privacy of all patients.
Lack of Transparency and Explainability
AI systems can be complex and opaque, often functioning as “black boxes” where the internal decision-making processes are not easily understood by users. This lack of transparency can create privacy concerns, as patients and healthcare providers may not fully understand how their data is being used or what decisions are being made based on it.
Without clear explanations of how AI systems process and interpret data, patients may be uneasy about the security and privacy of their information. Transparency in AI decision-making processes is crucial for building trust and ensuring that patients are informed about how their data is used. Developing explainable AI models that provide clear and understandable insights into their operations can help address these concerns and enhance data privacy.
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
The ethical and regulatory landscape surrounding AI and health data privacy is complex and evolving. Different jurisdictions have varying regulations and standards for data protection, which can complicate compliance for organizations operating across borders. Navigating these regulations requires a thorough understanding of legal requirements and ongoing adjustments to meet changing standards.
Ethical considerations also play a significant role in managing health data privacy. Ensuring that AI systems are used responsibly and that patient consent is obtained for data collection and analysis is crucial for maintaining trust and safeguarding privacy. Healthcare organizations must establish clear policies and practices for data handling, consent, and patient rights to address these ethical and regulatory challenges effectively.
Mitigating Privacy Risks and Ensuring Security
To address the drawbacks of AI in health data privacy, several measures can be taken to enhance security and protect patient information. Implementing robust encryption protocols, securing data storage and transmission, and conducting regular security audits are essential for safeguarding health data from breaches.
Moreover, adopting privacy-by-design principles in the development of AI systems can help ensure that data protection is integrated into the technology from the outset. This approach involves incorporating privacy considerations into every stage of AI development, from data collection and processing to model training and deployment.
Engaging with patients and stakeholders to provide clear information about how their data is used and ensuring that they have control over their information can also help build trust and address privacy concerns. Transparency, informed consent, and patient empowerment are key components in mitigating privacy risks and ensuring ethical AI practices.
Conclusion
While AI offers substantial benefits for healthcare, its use in managing health data brings significant privacy concerns. The increased risk of data breaches, challenges with data management and interoperability, potential for algorithmic bias, and lack of transparency pose serious drawbacks. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that includes robust cybersecurity measures, adherence to ethical and regulatory standards, and ongoing efforts to ensure transparency and fairness. By tackling these privacy concerns proactively, the healthcare industry can harness the power of AI while safeguarding patient information and maintaining trust in the digital age.